
The subfractionĮ2 showing more complicated profiles was separated to yield seven Subfraction E2 showed more diverse chemical profiles than E3, bothįractions had terpenoid-type components including sesquiterpenes andĭiterpenes as major proportions of overall profiles. Subfraction E1 confirmed what was predicted for phenolic compoundsĪnd flavonoids ( Figure S3). The SMART tool result of low cytotoxicity of Of the structures of the mixed components in the samples ( Figures Figures2 2B, S2, and S3). Into SMART 2.0 analysis ( ), which resulted in the prediction The HSQC NMRĭata of the subfractions E1, E2, and E3, were measured for the introduction Showed the most potent cytotoxic activities of 16.3–32.1 andġ5.7–31.6%, respectively, at a concentration of 100 μg/mLĪgainst five cancer cell lines and were expected to contain the anticancerĬompounds of E. Among the subfractions, E1 ∼ 5, E2, and E3, To normal column chromatography and fractionated into five subfractions Was expected to contain the cytotoxic constituents, was subjected (A549, MCF-7, HEp-2, SKOV3, and PC3) at a concentration 100 μg/mL Showed the most potent cytotoxic activity against 5 cancer cell lines fortunei, the total extract was fractionated into n-hexane, EtOAc, n-BuOH, and H 2O fractions, sequentially. Targeted isolation of the cytotoxic sesquiterpene lactones from E. Of the target compounds, which are expected to have biological activities.Ĭonsequently, we succeeded in the isolation of 10 sesquiterpene lactones
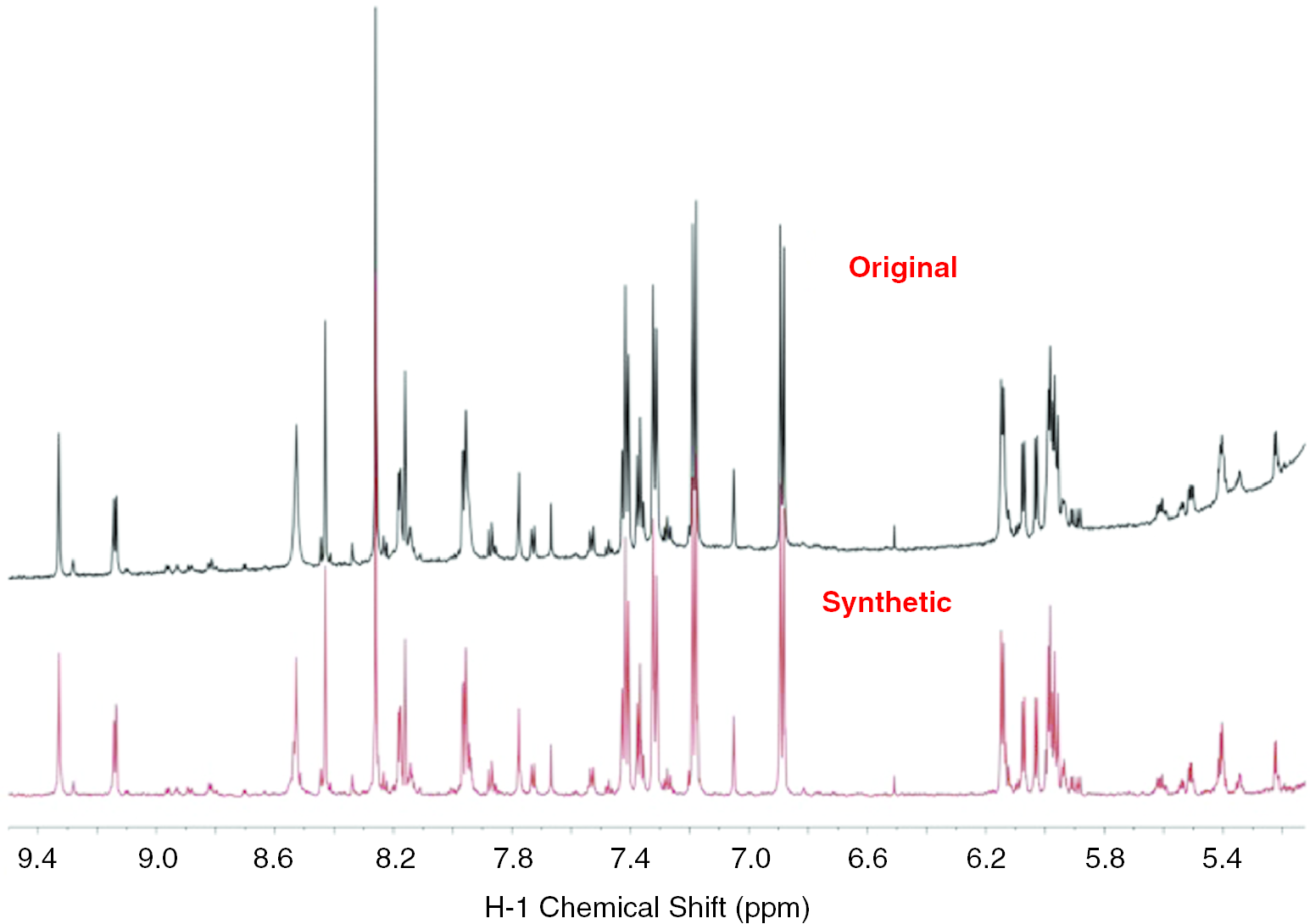
SMART 2.0 tool, to rapidly discover the targeted compounds in theĮxtract of a natural product and tried NMR spectra-guided isolation 16, 17 In the present study, we utilized the state-of-art technique, the Monocyclic ring with a cyclic ester structure. Tried to isolate germacrane-type sesquiterpene lactones having 10-membered fortunei, which is native to Korea, and especially Metabolites, such as alkaloids, 10 phenolicĪcids, 11 benzofuran, 12 triterpenoids, 13 and sesquiterpenes, 14 has been reported as the constituents foundĭiscovery of cytotoxic sesquiterpene lactones from Eupatorium species, 15 we focused on E. Eupatorium fortunei has been used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of cold,ĭropsy, chills, and fevers. Is widely distributed in Southeast Asian countries, such as Korea, Targeted compounds in the natural product research. We expected this tool to help in simplifying theĭereplication step and provide the bypass for the isolation of the 6, 7 SMART 2.0 trained on 1H- 13C HSQC spectralĭata of tons of natural products provided the insights for elucidating Introduced as the NMR-based machine learning study for the structuralĪnnotation of compounds in mixtures or unknown compounds. Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART 2.0) has been Reproducibility compared to MS, but it also needs to acquire expertiseįor the interpretation of 1D and 2D NMR data, which has become a bigīarrier for novice chemists in the fields of natural products. 5 Meanwhile, NMR spectroscopy guarantees higher The weak points for the accurate identification of compounds. Of tons of metabolites and production of their structural data inĪ short time, low reproducibility and interpretability have become 1− 4 Although high-resolution MS is the powerful technique for the measurement Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS), whichĪre the two most popular techniques for characterizing natural products,Īre being developed. In silico methods for spectrometric data generated using Product chemists have shown interest in the development of new in silico approaches for the rapid annotation of novel compoundsĪnd dereplication of the known ones from natural products. In natural products have hindered the discovery of novel druggable New insights for the development of therapeutic agents. Tool helped the targeted isolation of bioactive compounds from naturalīeen spotlighted as potential sources providing The mixture of compounds in a fraction by the NMR-based machine learning

In the present study, the rapid annotation of With IC 50 values of 5.8 ± 0.1 μM against breastĬancer cells, MCF-7. ± 1.2 and 3.9 ± 0.6 μM against prostate cancer cells, Compounds 4 and 8 exhibited IC 50 values of 3.9 fortunei obtained by SMART 2.0, their cytotoxic activities were evaluatedĪgainst five cancer cells (SKOV3, A549, PC3, HEp-2, and MCF-7). Of the results of the subfractions from E. ( 8 and 9) were isolated from the whole plant Eight germacrene-type ( 1–7 and 10) and two eudesmane-type sesquiterpene lactones Targeted isolation of sesquiterpene lactones from Eupatoriumįortunei with the aid of structural annotation by

The discovery and characterization of natural products. Recently been introduced as a NMR-based machine learning tool for Molecular Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART 2.0) has


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
